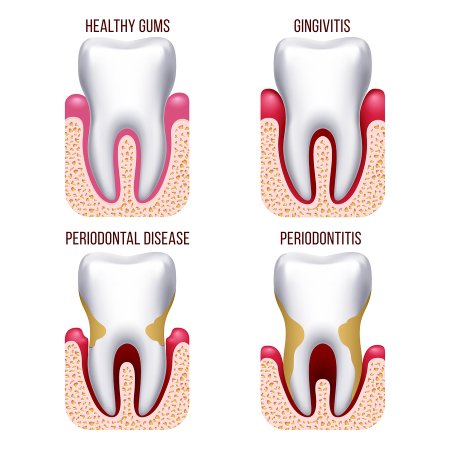
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is a common oral health problem that affects millions of people globally. It is a bacterial infection that damages the gum tissue and the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to inflammation, bleeding, and eventually tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Disease
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is one of the leading causes of gum disease. When plaque and tartar build up on the teeth and gums, it creates an environment where bacteria can thrive and cause inflammation and damage to the gum tissue.
2. Tobacco Use
Tobacco use, in any form, increases the risk of gum disease by reducing blood flow to the gums and suppressing the immune system. This makes it harder for the gums to fight off bacterial infections and heal properly.
3. Certain Medications
Certain medications, such as those that reduce saliva production, can also increase the risk of gum disease by creating a dry mouth environment where bacteria can thrive.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, menopause, and puberty, can also affect gum health and increase the risk of gum disease.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
1. Swelling or Tenderness
If you have gum disease, you may experience swelling or tenderness in the gums.
2. Gums that Bleed Easily
Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing is also a common symptom of gum disease.
3. Receding Gums
Gum disease can also cause the gums to recede, or pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive.
4. Bad Breath
Bad breath, or halitosis, is another symptom of gum disease.
Diagnosing Gum Disease
1. Clinical Exam
A clinical exam is the first step in diagnosing gum disease. During this exam, a dentist will visually examine the gums and teeth for signs of swelling, tenderness, and bleeding.
2. X-rays
X-rays can provide a detailed view of the supporting structures of the teeth and can help identify any damage caused by gum disease.
3. Blood Tests
Blood tests can also be used to check for markers of inflammation and infection in the gums.
Treating Gum Disease
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
The first line of treatment for gum disease is a professional dental cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing. This procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line, and smoothing the root surfaces to discourage the buildup of future plaque.
2. Medication
Medication, such as antibiotics, can also be used to help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the gums.
3. Surgery
In severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged gum tissue and bone.
Prevention of Gum Disease
1. Regular Brushing and Flossing
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including brushing at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily, is essential for preventing gum disease.
2. Avoiding Tobacco Use
Avoiding tobacco use, in any form, is also crucial in preventing gum disease. Tobacco use increases the risk of gum disease by reducing blood flow to the gums and suppressing the immune system.
3. Regular Dental Visits
Visiting a dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups is another important step in preventing gum disease. During these visits, a dentist can remove plaque and tartar buildup, check for signs of gum disease, and provide recommendations for maintaining good oral hygiene.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum health is an essential aspect of oral hygiene that should not be overlooked. By understanding the causes and symptoms of gum disease, taking steps to prevent it, and seeking proper treatment if necessary, you can help maintain the health and stability of your teeth and gums. For more information on gum health, consult with a dentist or visit the American Dental Association’s website.